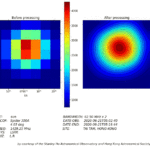
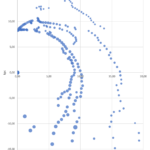
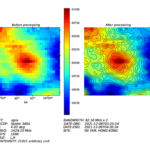
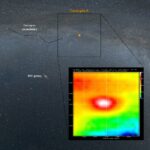
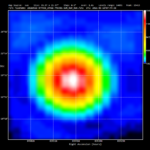
Affordable radio interferometry with SPIDER MarkII radio telescopes
Radio interferometry is the technique used by professional radio astronomers to create a single large radio telescope using multiple smaller antennas. Radio interferometry allows radio astronomers to obtain radio pictures with higher angular resolution, but up until now this technique has been used only in very expensive research instruments….